The Importance of Refrigerated Containers in the Transport of Perishables
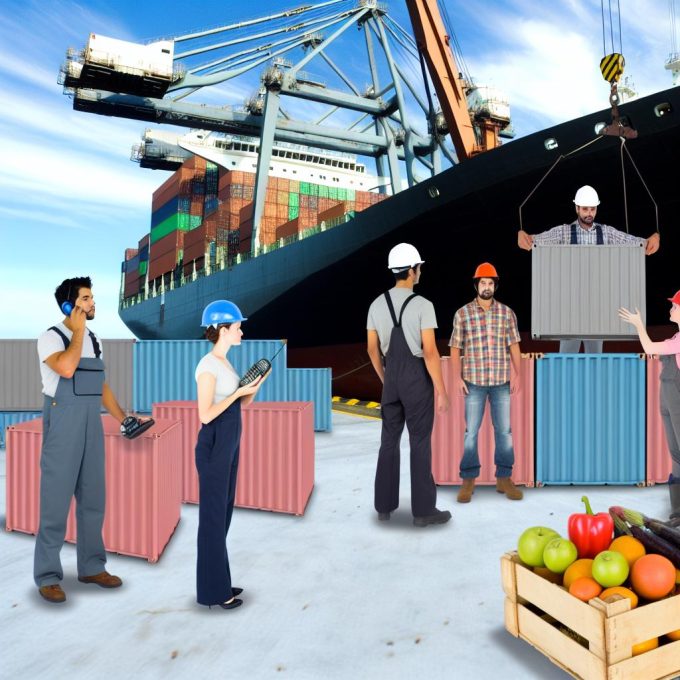
Refrigerated containers, commonly known as reefers, are a cornerstone of the global logistics network, particularly in the transportation of perishable goods. These specially designed shipping containers are engineered to maintain a specific and controlled temperature range, ensuring that perishable items like fruits, vegetables, meats, and pharmaceuticals arrive at their destination in optimal condition. This article delves into the intricacies of how these containers function, their impact on global trade, the economic and environmental considerations they encapsulate, and the continuous innovations shaping their future.
How Reefers Function
Reefers are integral to the logistics of transporting temperature-sensitive goods over long distances. They are equipped with a built-in refrigeration unit that runs on external power sources, such as those available at ports or on ships. This refrigeration system leverages advanced cooling technologies to maintain a stable and precise temperature. Depending on the type of goods being transported, reefers can be programmed to support a wide array of temperatures, ranging from deep freeze conditions suitable for meats to a slight chill for other perishables.
Temperature Control
The ability to control the temperature precisely is fundamental to the success of transporting perishable goods. Many such goods, including fresh produce, dairy products, meats, and pharmaceuticals, require a specific climatic environment to retain their freshness, efficacy, or quality. If these conditions are not maintained accurately, it could lead to significant financial losses due to spoilage or a drop in product quality. For example, produce that is too warm may over-ripen, while pharmaceuticals stored at incorrect temperatures may lose their effectiveness. Thus, temperature control is a critical feature that enables the safe and efficient transport of these sensitive goods.
Ventilation
An additional essential function of reefers is ventilation. Effective ventilation systems are crucial to prevent the buildup of ethylene gas and other ripening agents inside the container. This is particularly important for ethylene-sensitive produce, such as apples and bananas, which could spoil prematurely if exposed to high concentrations of these gases. During long journeys, the internal environment of the reefer must be meticulously managed to minimize the risk of spoilage. Ventilation systems ensure that the air circulation within the container is consistent, thus preserving the quality and extending the shelf life of the transported goods.
Global Trade Impact
The introduction and widespread use of refrigerated containers have had profound implications for global trade. By facilitating the efficient long-distance transport of perishable goods, reefers effectively bridge the gap between producers and consumers spread across continents. This capability is critically important for countries that depend heavily on the export of agricultural produce. With reefers, they can access international markets without compromising the quality of their products. Freshness and quality are crucial selling points in international trade, and reefers ensure these attributes are maintained throughout transit.
Economic Benefits
From an economic perspective, the use of refrigerated containers offers numerous benefits to producers and exporters. By preserving the quality and extending the life cycle of goods, reefers help sustain product value, thereby supporting the profitability of trade and enhancing market competitiveness. When exporters can guarantee the delivery of goods in peak condition, they not only fulfill buyer expectations but also avoid the financial losses associated with rejected shipments or discounts due to degradation in quality. As a result, both producers and buyers gain confidence in the logistic chain, encouraging more robust trade relations.
Environmental Considerations
While the use of reefers plays a vital role in international trade, it also presents environmental challenges primarily related to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional reefer systems depend on significant quantities of energy, often sourced from fossil fuels, to maintain precise temperature control. This energy use results in a substantial carbon footprint. However, recent advancements in technology have led to more energy-efficient refrigeration solutions, thereby reducing emissions. Innovations such as solar-powered reefers, improved insulation materials, and optimized refrigeration cycles are paving the way toward more sustainable practices in refrigerated transport. Continued research and development in this field are essential to reduce the environmental impact of reefers without compromising their functionality.
Conclusion
Refrigerated containers are vital to the modern supply chain, offering indispensable solutions for the transportation of temperature-sensitive goods. As global demand for fresh produce, pharmaceuticals, and other perishables continues to increase, the role of reefers in maintaining the quality and safety of these items during transit is more critical than ever. The sustained innovation in reefer technology and logistics strategies is crucial to address future challenges expected in the perishable goods market. Stakeholders in the transportation and logistics sectors must continually assess and adopt new technologies and practices to ensure efficient and environmentally responsible refrigerated transport. In doing so, they not only safeguard the quality of transported goods but also contribute to more sustainable global trade practices.